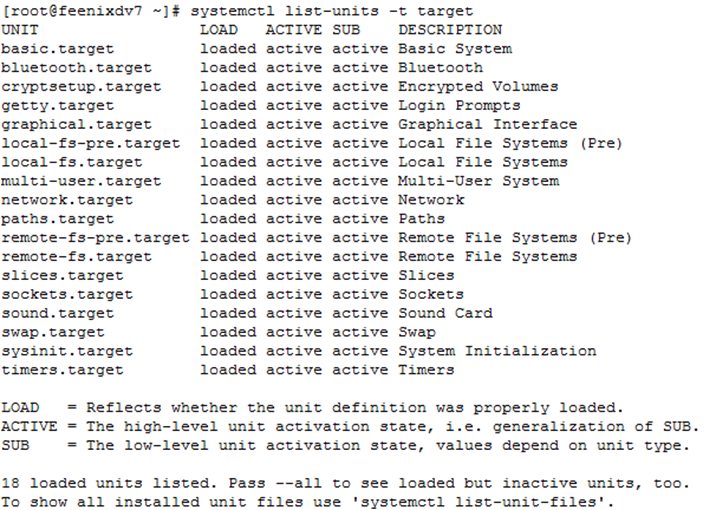
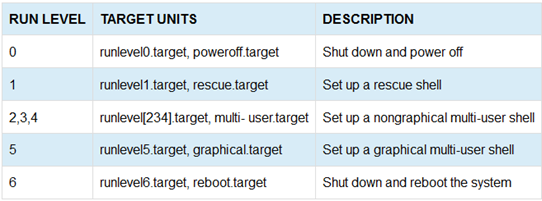
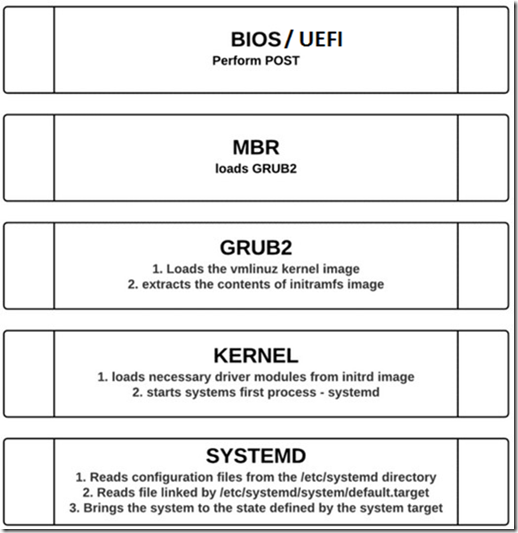
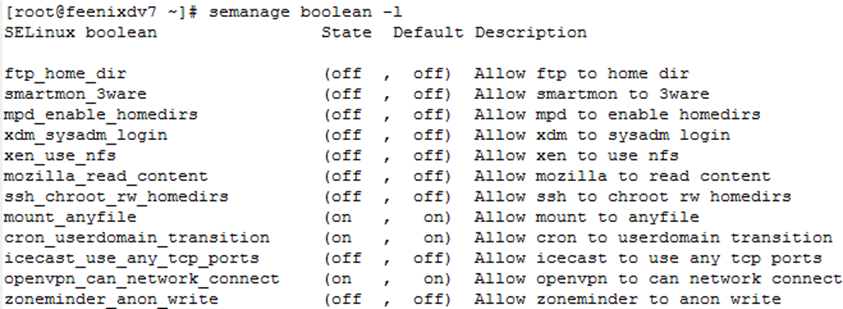
New features in Apache HTTP Server 2.4
|
|
Core Enhancements
--enable-mpms-shared=all
Default: LogLevel warn
Default: KeepAliveTimeout 5
None and AllowOverride is set to None, then .htaccess files are completely ignored. In this case, the server will not even attempt to read .htaccess files in the filesystem.
Redirect and RedirectMatch directives are allowed. All others will cause an Internal Server Error.
New Modules
mod_lua
Embeds the Lua language into httpd, for configuration and small business logic functions. (Experimental)
mod_log_debug
Allows the addition of customizable debug logging at different phases of the request processing.
mod_buffer
Provides for buffering the input and output filter stacks
mod_data
Convert response body into an RFC2397 data URL
mod_ratelimit
Provides Bandwidth Rate Limiting for Clients
mod_request
Provides Filters to handle and make available HTTP request bodies
mod_reflector
Provides Reflection of a request body as a response via the output filter stack.
mod_slotmem_shm
Provides a Slot-based shared memory provider (ala the scoreboard).
mod_xml2enc
Formerly a third-party module, this supports internationalization in libxml2-based (markup-aware) filter modules.
mod_macro (available since 2.4.5)
Provide macros within configuration files.
mod_proxy_wstunnel (available since 2.4.5)
Support web-socket tunnels.
mod_authnz_fcgi (available since 2.4.10)
Enable FastCGI authorizer applications to authenticate and/or authorize clients.
mod_http2 (available since 2.4.17)
Support for the HTTP/2 transport layer.
mod_proxy_hcheck (available since 2.4.21)
Support independent dynamic health checks for remote proxiy backend servers.
Module Enhancements
mod_ssl
mod_ssl can now be configured to use an OCSP server to check the validation status of a client certificate. The default responder is configurable, along with the decision on whether to prefer the responder designated in the client certificate itself.
mod_ssl now also supports OCSP stapling, where the server pro-actively obtains an OCSP verification of its certificate and transmits that to the client during the handshake.
mod_ssl can now be configured to share SSL Session data between servers through memcached
EC keys are now supported in addition to RSA and DSA.
Support for TLS-SRP (available in 2.4.4 and later).
mod_proxy
The ProxyPass directive is now most optimally configured within a Location or LocationMatch block, and offers a significant performance advantage over the traditional two-parameter syntax when present in large numbers.
The source address used for proxy requests is now configurable.
Support for Unix domain sockets to the backend (available in 2.4.7 and later).
mod_proxy_balancer
More runtime configuration changes for BalancerMembers via balancer-manager
Additional BalancerMembers can be added at runtime via balancer-manager
Runtime configuration of a subset of Balancer parameters
BalancerMembers can be set to 'Drain' so that they only respond to existing sticky sessions, allowing them to be taken gracefully offline.
Balancer settings can be persistent after restarts.
mod_cache
The mod_cache CACHE filter can be optionally inserted at a given point in the filter chain to provide fine control over caching.
mod_cache can now cache HEAD requests.
Where possible, mod_cache directives can now be set per directory, instead of per server.
The base URL of cached URLs can be customized, so that a cluster of caches can share the same endpoint URL prefix.
mod_cache is now capable of serving stale cached data when a backend is unavailable (error 5xx).
mod_cache can now insert HIT/MISS/REVALIDATE into an X-Cache header.
mod_include
Support for the 'onerror' attributes within an 'include' element, allowing an error document to be served on error instead of the default error string.
mod_cgi, mod_include, mod_isapi, …
Translation of headers to environment variables is more strict than before to mitigate some possible cross-site-scripting attacks via header injection. Headers containing invalid characters (including underscores) are now silently dropped. Environment Variables in Apache has some pointers on how to work around broken legacy clients which require such headers. (This affects all modules which use these environment variables.)
mod_authz_core Authorization Logic Containers
Advanced authorization logic may now be specified using the Require directive and the related container directives, such as <RequireAll>.
mod_rewrite
mod_rewrite adds the [QSD] (Query String Discard) and [END] flags for RewriteRule to simplify common rewriting scenarios.
Adds the possibility to use complex boolean expressions in RewriteCond.
Allows the use of SQL queries as RewriteMap functions.
mod_ldap, mod_authnz_ldap
mod_authnz_ldap adds support for nested groups.
mod_ldap adds LDAPConnectionPoolTTL, LDAPTimeout, and other improvements in the handling of timeouts. This is especially useful for setups where a stateful firewall drops idle connections to the LDAP server.
mod_ldap adds LDAPLibraryDebug to log debug information provided by the used LDAP toolkit.
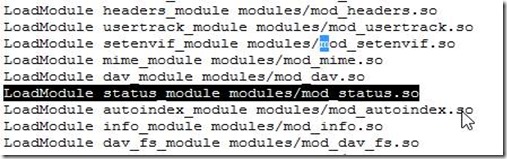
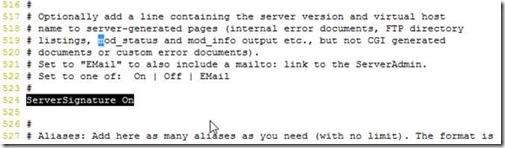
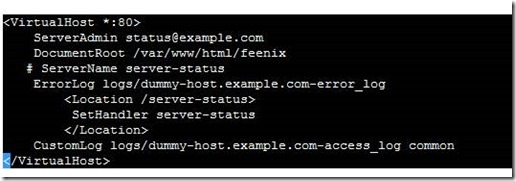
mod_info
mod_info can now dump the pre-parsed configuration to stdout during server startup.
mod_auth_basic
New generic mechanism to fake basic authentication (available in 2.4.5 and later).
Program Enhancements
fcgistarter
New FastCGI daemon starter utility
htcacheclean
Current cached URLs can now be listed, with optional metadata included.
Allow explicit deletion of individual cached URLs from the cache.
File sizes can now be rounded up to the given block size, making the size limits map more closely to the real size on disk.
Cache size can now be limited by the number of inodes, instead of or in addition to being limited by the size of the files on disk.
rotatelogs
May now create a link to the current log file.
May now invoke a custom post-rotate script.
htpasswd, htdbm
Support for the bcrypt algorithm (available in 2.4.4 and later).
Documentation
mod_rewrite
The mod_rewrite documentation has been rearranged and almost completely rewritten, with a focus on examples and common usage, as well as on showing you when other solutions are more appropriate. The Rewrite Guide is now a top-level section with much more detail and better organization.
mod_ssl
The mod_ssl documentation has been greatly enhanced, with more examples at the getting started level, in addition to the previous focus on technical details.
Caching Guide
The Caching Guide has been rewritten to properly distinguish between the RFC2616 HTTP/1.1 caching features provided by mod_cache, and the generic key/value caching provided by the socache interface, as well as to cover specialized caching provided by mechanisms such as mod_file_cache.
Take reference from apache.org







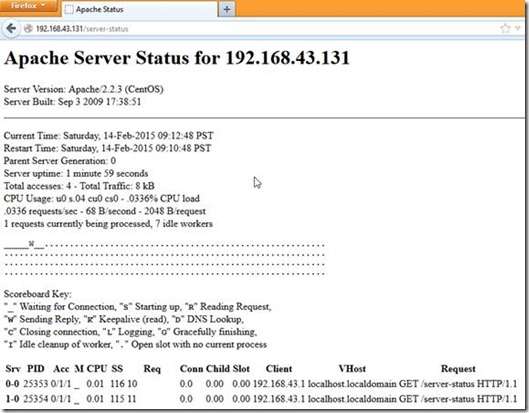



![image_thumb[3] image_thumb[3]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/image_thumb3_thumb.png)
![image_thumb[6] image_thumb[6]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/image_thumb6_thumb.png)
![image_thumb[11] image_thumb[11]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/image_thumb11_thumb.png)
![image_thumb[15] image_thumb[15]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/image_thumb15_thumb.png)
![image_thumb[19] image_thumb[19]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/image_thumb19_thumb.png)
![image_thumb[23] image_thumb[23]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/image_thumb23_thumb.png)

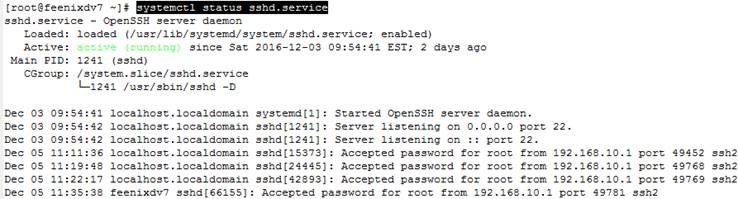
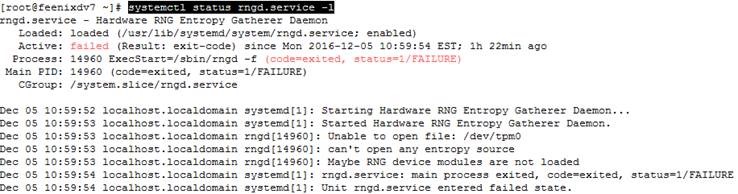


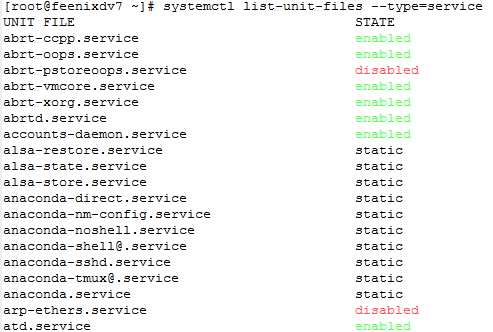
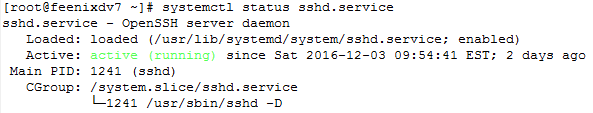
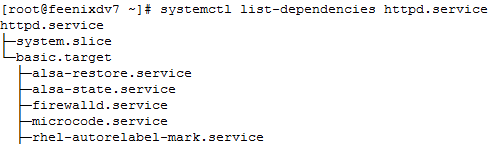

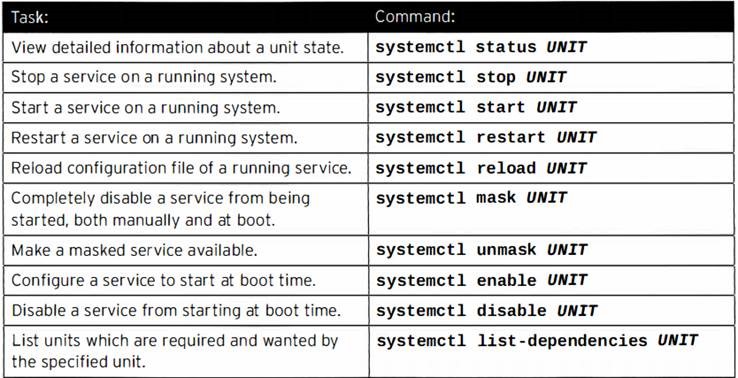
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0014_thumb-2.png)

![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0024_thumb-2.png)
![clip_image003[4] clip_image003[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0034_thumb-2.png)
![clip_image005[4] clip_image005[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0054_thumb-2.png)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0014_thumb-1.png)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0024_thumb-1.png)
![clip_image003[4] clip_image003[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0034_thumb-1.png)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0044_thumb-1.png)
![clip_image005[4] clip_image005[4]](https://feenixdv.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/clip_image0054_thumb-1.png)